Policymakers in some of the world’s largest economies are reducing support for solar power generation. Even so, Goldman Sachs Research expects rapid growth in the sector, with global solar installations set to rise to 914 Gigawatts (Gw) in 2030, 57% above 2024 levels.
Compared to other sources of power, “the rise in solar generation is the fastest in the history of electricity,” says Daan Struyven, co-head of global commodities research at Goldman Sachs Research. Solar generation has reached 2,129 Terawatt-hours (Twh) in 11 years since taking off, and it has driven 8% of global power generation over the 12 months leading to July 2025.
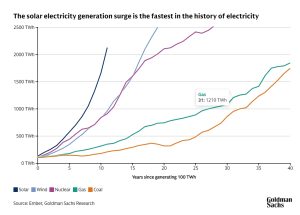
While the US and China have reduced support for the sector, solar energy is still likely to meet a high share of global energy demand in the long run.
The challenges of solar power
The solar industry can run into mismatches between demand and supply, as when excess energy fed into the grid causes wholesale power prices to turn negative—a phenomenon common in Australia and California. When solar energy, together with wind energy, forms a high share of power generation in a grid, any excess swings in power frequency can lead to blackouts, as seen in Spain and Portugal this past April.
Recent government policies also pose new challenges to the industry. China has removed grid access for all new large-scale commercial and industrial solar projects. New Chinese renewable power projects are also not guaranteed minimum purchase prices or grid volumes anymore.
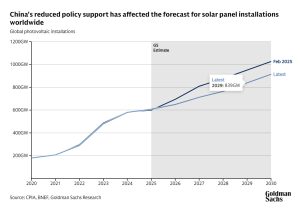
Struyven adds that, in the US, his team doesn’t expect the diminishment of policy support “to significantly weigh on solar power developments until 2030, because most projects have or will benefit from the safe harbor provision to qualify for tax credits ahead of the mid-2026 deadline.” That said, Struyven writes, “the federal government’s ongoing review of the implementation rules poses downside risk to solar installations from 2028.”
The drivers of the solar energy boom
Despite these challenges, Struyven’s team identifies three structural factors that are likely to sustain a rapid growth in the solar sector.
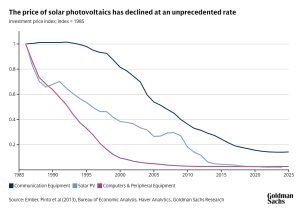
First, the cost of solar panels drops fast as the industry makes more of them. Our analysts estimate that costs tend to fall 20% if cumulative output doubles, with a positive feedback loop from lower costs to higher demand, higher supply, and again lower costs. “The investment costs have fallen faster for panels than for any other investment good in modern history, including computers and communication equipment,” Struyven writes.
Second, solar energy’s marginal fuel costs are zero, meaning that it costs nothing to produce every additional unit of electricity beyond the original cost of installing the panels and the ongoing cost of maintaining them.
Third, solar panels are modular: They come in small sizes available at constant fixed prices, making it easier to create a decentralized grid. In contrast, thermal or nuclear power stations are usually large with high fixed costs.
Bottlenecks in solar panel supply are unlikely, in part because there is plenty of excess capacity in the sector, with China’s production potential alone covering 200% of global demand in 2024. “Any slowing in solar growth is likely to come from reduced policy support and from power supply volatility rather than from solar panel supply bottlenecks,” says Struyven.





